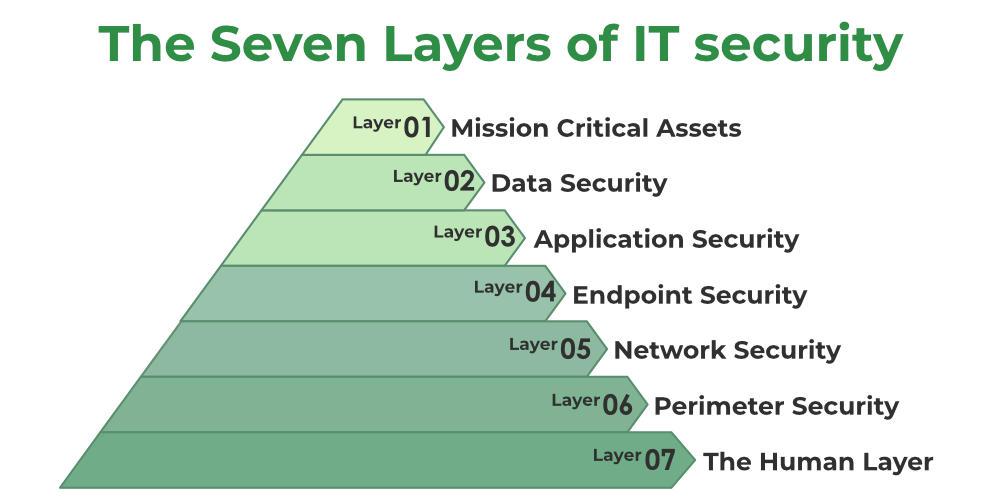
The 7 layers of cyber security include physical security, network security, perimeter security, endpoint security, application security, data security, and user awareness. Cyber security is essential for protecting digital assets from threats.
These 7 layers form a comprehensive defense strategy. Physical security safeguards hardware. Network security defends against unauthorized access. Perimeter security includes firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Endpoint security protects individual devices. Application security ensures software integrity. Data security involves encryption and access controls.
User awareness educates on best practices and threat recognition. Each layer addresses specific vulnerabilities, creating a robust defense. Understanding these layers helps in implementing effective security measures. This multi-layered approach is crucial in today’s threat landscape.
Introduction To Cyber Security Layers
Cyber security layers protect our digital world from threats. Each layer adds an extra line of defense. Together, they form a strong shield against cyber attacks. Understanding these layers helps keep our data safe.
Importance Of Multi-layered Security
Multi-layered security uses multiple defenses to protect systems. If one layer fails, others are still there. This approach reduces the chance of a successful attack. It also helps in quickly identifying threats.
Overview Of The Seven Layers
The seven layers of cyber security cover different aspects of protection. Each layer focuses on specific threats and vulnerabilities. Here is an overview:
- Physical Security: Protects hardware from physical threats.
- Network Security: Secures the data traveling over networks.
- Perimeter Security: Defends the boundary between the network and outside world.
- Endpoint Security: Safeguards individual devices like computers and mobile phones.
- Application Security: Secures software applications from cyber threats.
- Data Security: Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- User Education: Teaches users to recognize and avoid cyber threats.
Each layer works together to create a robust cyber security strategy. Protecting our digital lives requires understanding and implementing these layers effectively.

Layer 1: Physical Security
Physical security is the first layer of cyber security. It safeguards hardware and infrastructure. Without it, other security measures fail.
Access Control
Access control prevents unauthorized access to sensitive areas. Use locks, badges, and biometric scans to secure entry points. Only authorized personnel should enter secured zones. This minimizes risks and protects assets.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Locks | Simple but effective. Require keys or codes. |
| Badges | Grant access with ID badges. Monitor movement. |
| Biometric Scans | Use fingerprints or retina scans. High-level security. |
Environmental Controls
Environmental controls protect physical infrastructure from damage. Use fire suppression systems to prevent fire damage. Install air conditioning to keep equipment cool. Ensure humidity levels are controlled. This prevents corrosion and damage.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Use sprinklers or gas systems.
- Air Conditioning: Maintain optimal temperature for equipment.
- Humidity Control: Keep humidity at safe levels. Prevent corrosion.
Physical security forms the foundation of cyber security. Without it, systems remain vulnerable.
Layer 2: Network Security
Network security is the second layer of cyber security. It focuses on protecting the integrity of your network. This layer ensures that unauthorized users do not gain access. Two main components of network security are Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems.
Firewalls
A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and potential threats. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls use predefined security rules to filter traffic. They help in blocking unauthorized access while permitting legitimate communication.
There are different types of firewalls:
- Packet-filtering Firewalls: Inspect packets and block them if they don’t meet security criteria.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: Monitor the state of active connections and decide which network packets to allow through.
- Proxy Firewalls: Serve as an intermediary between end-users and the web, providing additional security features.
Intrusion Detection Systems
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is designed to detect suspicious activity. IDS monitors network traffic for unusual behavior or known threats. When it identifies a potential threat, it alerts the network administrator. IDS can be classified into two main types:
- Network-based IDS (NIDS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Host-based IDS (HIDS): Monitors a single host for suspicious activity.
IDS helps in identifying possible security breaches, including both intrusions (attacks from outside the organization) and misuse (attacks from within the organization).
Proper implementation of firewalls and IDS can significantly enhance your network security. Combining these tools provides a robust defense against various cyber threats.
Layer 3: Endpoint Security
Layer 3: Endpoint Security is crucial in protecting devices connected to your network. This layer ensures that individual devices, like laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are secure from cyber threats. By securing endpoints, you reduce the risk of attacks on your network.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is essential for endpoint security. It scans files and programs for malware and other threats. Regular updates keep the software effective against new viruses.
- Scans files and programs for malware
- Provides real-time protection
- Offers regular updates to combat new threats
Using antivirus software, you protect your device from harmful threats. This keeps your data secure and your device running smoothly.
Device Management
Device management involves overseeing and securing all devices connected to your network. This includes implementing policies and monitoring device activity.
| Device Management Tasks | Description |
|---|---|
| Policy Implementation | Set rules for device usage and access. |
| Activity Monitoring | Track device activity for unusual behavior. |
| Regular Updates | Ensure devices have the latest security patches. |
Effective device management reduces the risk of breaches and unauthorized access. By monitoring devices, you can quickly respond to threats.
Layer 4: Application Security
In the modern world, application security is crucial. It protects software applications from threats. This layer focuses on securing the application’s code. It prevents unauthorized access and data breaches.
Secure Coding Practices
Secure coding practices are essential for creating safe applications. Developers must follow guidelines to write secure code. These practices help in reducing vulnerabilities. Some key practices include:
- Validating user inputs
- Using strong authentication methods
- Implementing proper error handling
- Encrypting sensitive data
By following these practices, developers can build robust applications. These applications can withstand various cyber threats.
Application Testing
Application testing ensures the software is secure. It identifies and fixes vulnerabilities before deployment. Testing methods include:
- Static code analysis
- Dynamic code analysis
- Penetration testing
- Security audits
These methods help in finding security flaws in the application. Regular testing is vital for maintaining application security.
A combination of secure coding practices and application testing makes Layer 4 strong. This ensures the application remains safe from cyber threats.
Layer 5: Data Security
Data Security is the fifth layer in the 7 layers of cyber security. Its primary goal is to protect data from unauthorized access and corruption. This layer ensures sensitive data remains safe and confidential.
Encryption
Encryption is a vital part of data security. It transforms readable data into an unreadable format. Only those with the correct key can decode it. This process ensures data remains private and secure. Even if attackers intercept the data, they can’t read it without the key.
Data Loss Prevention
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools help prevent data breaches. DLP ensures sensitive data is not lost, misused, or accessed by unauthorized users. These tools monitor and control data transfers. They can block risky activities and alert administrators. DLP tools are essential for protecting sensitive information.
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Protects data from unauthorized access |
| Data Loss Prevention | Prevents data breaches and misuse |
Both encryption and DLP are crucial for data security. They ensure data remains safe and private.
Layer 6: Identity And Access Management
Layer 6 of cyber security focuses on Identity and Access Management (IAM). This layer ensures that the right individuals have access to the right resources at the right times. Effective IAM solutions minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
User Authentication
User Authentication verifies the identity of a user. It ensures that users are who they claim to be. Common methods of user authentication include:
- Passwords: The most basic form of authentication.
- Biometrics: Uses fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Combines passwords with another factor, like a code sent to a phone.
Using strong authentication methods reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Regularly updating and reviewing authentication methods is crucial.
Access Controls
Access Controls determine what resources a user can access. These controls ensure that users only have access to what they need. Key types of access controls include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Permissions are assigned based on user roles. |
| Mandatory Access Control (MAC) | Access is based on regulations and policies. |
| Discretionary Access Control (DAC) | Owners of resources decide who has access. |
Implementing robust access controls helps protect sensitive data. Regular audits of access controls ensure that only authorized users have access.
By focusing on Identity and Access Management, organizations can greatly enhance their cyber security posture.

Layer 7: Security Policies And Procedures
Layer 7 focuses on Security Policies and Procedures. This layer ensures that a company has clear guidelines and rules. These rules help maintain a secure environment. Policies and procedures act as a framework for all security measures.
Incident Response Plan
An Incident Response Plan outlines steps to take during a security breach. It prepares the team to handle incidents quickly and efficiently. The plan includes:
- Identifying the incident
- Containing the breach
- Eradicating the threat
- Recovering affected systems
- Reviewing and learning from the incident
Having a solid incident response plan reduces damage and recovery time. It ensures everyone knows their role during a crisis.
Compliance And Auditing
Compliance and Auditing ensure the organization meets legal and regulatory requirements. Regular audits help identify gaps in security policies. They ensure the company follows all necessary laws.
Key components include:
- Understanding relevant regulations
- Implementing necessary controls
- Conducting regular audits
- Documenting and reporting findings
Compliance protects the company from legal issues and fines. Auditing helps maintain a high level of security.
Future Trends In Cyber Security
The future of cyber security is evolving rapidly. New threats emerge daily, demanding advanced solutions. Experts predict revolutionary trends. Let’s explore two key trends shaping the future of cyber security.
Ai And Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming cyber security. They analyze vast amounts of data quickly. This helps identify threats faster than humans. AI and ML also adapt to new threats. They learn from past attacks to improve future responses.
Benefits of AI and ML in cyber security:
- Real-time threat detection: AI can spot threats as they happen.
- Enhanced data analysis: ML processes large datasets efficiently.
- Automated responses: AI can take action without human intervention.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is another trend in cyber security. The principle is simple: Trust no one. Verify everyone. This approach secures networks by limiting access. Users must prove their identity at every step. This reduces the risk of insider threats.
Key features of Zero Trust Architecture:
- Continuous verification: Users are verified constantly.
- Least privilege access: Users get minimal access rights.
- Micro-segmentation: Networks are divided into smaller zones.
Adopting these trends can significantly enhance cyber security. Stay ahead of threats with AI, ML, and Zero Trust Architecture. Protect your data and systems effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The 7 Layers Of Cyber Security?
The 7 layers of cyber security include: Physical, Network, Perimeter, Endpoint, Application, Data, and User. Each layer provides distinct protections.
Why Is Network Security Crucial?
Network security is crucial to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. It safeguards critical information from cyber threats.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
Endpoint security protects devices that connect to your network. It includes antivirus, anti-malware, and encryption to secure data.
What Is The Role Of Data Security?
Data security involves protecting data from unauthorized access and corruption. It ensures data privacy and compliance with regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding the 7 layers of cyber security is crucial for protecting digital assets. Implementing each layer enhances your defense strategy. Stay informed and updated on cyber threats. Protecting your data requires a proactive approach. Invest in robust security measures. This ensures a safer digital environment for your business and personal information.
